Spermatogenesis : Definition & Process ||Class 12 Biology
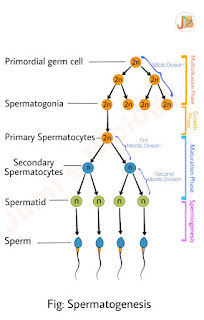
Spermatogenesis is the process of formation of spermatozoa (sperms) in the testes which originate from the primordial germ cells (PCGs).
The process of Spermatogenesis initiates at puberty and continues even in the old age.
The process of Spermatogenesis comprised the following two main stages-
1. Formation of spermatids
2. Spermiogenesis
1. Formation of spermatids: It include the following three phases-
i) Multiplication Phase
ii) Growth Phase
iii) Maturation Phase
i) Multiplication Phase: During this phase, the immature germ cells present in the Seminiferous tubules of the testes known as spermatogonia increases in number by mitotic divisions and so that the newly formed spermatogonium possesses the same number at chromosomes.
ii) Growth Phase: Each spermatogonium is diploid (2n) and contains 46 chromosomes. Some of the spermatogonia called primary spermatocytes.
iii) Maturation Phase: Primary spermatocytes periodically undergo meiosis division. A primary spermatocytes completes the first meiotic division (reduction division) leading to formation of two equal, heploid (n) cells called secondary spermatocytes, which contains only 23 chromosomes each. The secondary spermatocytes undergo the second meiotic division to produce four equal haploid spermatids.
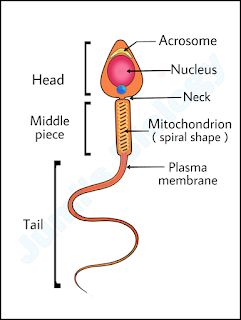
2. Spermiogenesis: It is the final stage of Spermatogenesis. The spermatids are transformed into spermatozoa (Sperms) by the process called spermiogenesis.

Well Organised
ReplyDeleteThank you so much 😊
DeleteThank you 😊
ReplyDeleteHelpful for students,good initiative. Keep it up
ReplyDeleteThank you so much 😊
DeleteNice
ReplyDeleteThank you 😊
DeleteMa'am Assamese ot dibo paribo nake
ReplyDeleteMa'am assamese tt dibo paribone
ReplyDeleteMam Assamese ot notes khini dib parib neki
ReplyDeleteThank you ma'am....
ReplyDeleteAssamamese nots please
ReplyDeleteMem Assamese notse diyok
ReplyDelete