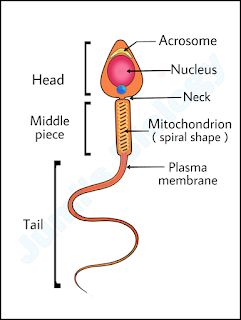
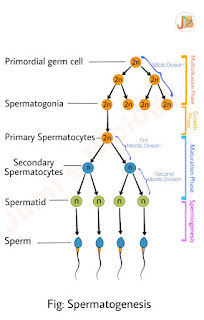
Colour Blindness: Causes & Symptoms ||Class 12 Biology
Colour blindness is a recessive sex-linked trait. The recessive allele are carried by X-chromosome. Colour blindness is also known as colour vision deficiency, is the decreased ability to see differences in colour. Red-green colour blindness is the most common form, followed by blue-yellow colour blindness and total colour blindness. In Red-green colour blindness, the affected eye fail to distinguish between red and green colours.
The ishihara colour test, which consists of a series of pictures of coloured spots, is the test most often used to diagnose red-green colour deficiencies.
Ishihara card
In female, it appears only when both the sex chromosome carry the gene (XcXc). The females function as carries in the presence of a single recessive gene (XXc) while in males the defects appears in the presence of a single recessive gene (XcY) because Y-chromosome does not carry any gene for colour vision.
There is no cure for colour blindness. Special lenses may help people with red-green colour blindness when under bright conditions.


Comments
Post a Comment
If you have any doubts,please let me know