Placenta: Structure & function ||Class 12 Biology
The placenta is an organ attached to the lining of womb during pregnancy.
Structure:
After implantation, finger-link projections appears on the trophoblast called chorionic villi which surrounded by the uterine tissues and maternal blood. The chorionic villi and the uterine tissue become interdigitated with each other and jointly form a structural and and functional unit between foetus and maternal body called placenta. Placenta is forms from the chorian and allantois. In human, the placenta averages 22cm (9 inch) in length and 2-2.5cm (0.8-1inch) in thickness. it has dark reddish-blue or crimson colour. It connects to the foetus by an umbilical cord.
Function:
1. It facilitates the supply of oxygen and nutrients to the embryo.
2. Responsible for the removal of carbon dioxide and waste materials produced by the foetus.
3. The placenta is connected to the embryo through the umbilical cord which helps in the transport of substances to and from the embryo.
4. It also act as an endocrine tissue by producing several hormones such as human Chronic Gonadotropin (hCG), human Placental Lactogen (hPL), estrogen and progesterone etc.

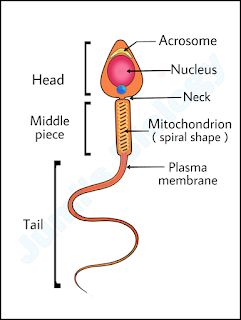
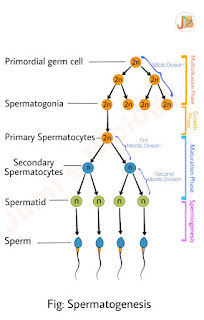

Informative
ReplyDeleteThank you 😊
DeleteThank you 😊
ReplyDelete