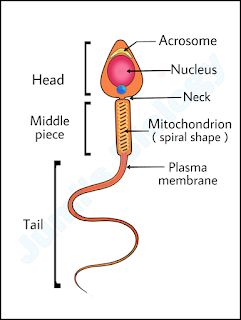
Mendel's Laws of Inheritance: Definitions & Examples ||Class 12 Biology
Based on Mendel observation, he proposed the following three main laws-
1. Law of Dominance (First Law)
2. Law of Segregation (Second Law)
3. Law of Independent Assortment (Third Law)
1.Law of Dominance:
According to the Mendel's first law of Inheritance, when two alternative forms of a trait or character (genes) are present in an organism, only one factor expresses itself in F1-progeny and is called dominant, where the other that remains hidden or masked is called recessive.
The law is used to explain the expression of only one of the parental characters in a monohybrid cross in the F1-generation and expression of both in the F2-generation. It also explains the reason for the proportion of 3:1 obtained in the F2-generation.
2.Law of Segregation:
According to the second law, Alleles do not show any blending (mixing of characters) and both the characters are recovered as such in the F2-generation, though one of these is not seen in the F1-generation.
Due to this, the gametes obtained are pure for a character. Though, the parents contain two alleles during gamete formation, the factors or alleles of a pair segregate from each other such that a gamete receives only one of the two factors.
3.Law of Independent Assortment:
According to the third Law of Mendel, when two pairs of traits are combined in a hybrid, segregation of one pair of a character is independent to that of the other pair of character at the time of gamete formation. These factors are randomly rearranged in the offsprings producing both parental and new (hybrid) combinations of characters.
The Punnett Square, can be used to understand the independent segregation of the two pairs of genes during meiosis. The law was proposed by Mendel, based on results of Dihybrid Crosses, where inheritance of two traits were consided simultaneously. The phenotypic ratio of Mendel's dihybrid cross is 9:3:3:1



Comments
Post a Comment
If you have any doubts,please let me know